What is Seibu's Unique Stone Lapping?
Seibu's Unique Stone Lapping
Seibu's unique stone lapping methods make optimal use of the characteristics of machine tools, lapping stones, and control systems; we have established our own unique stone lapping methods.
Our machine tools are built rigidly with minimal vibrations. Stones, with ultrafine abrasive diamond or CBN grains, are retained by rigid holders, and the stones are also rigid. The stones are oscillated (vibrated minutely) in parallel with workpieces under low pressure through the use of our uniquely developed air bearings.
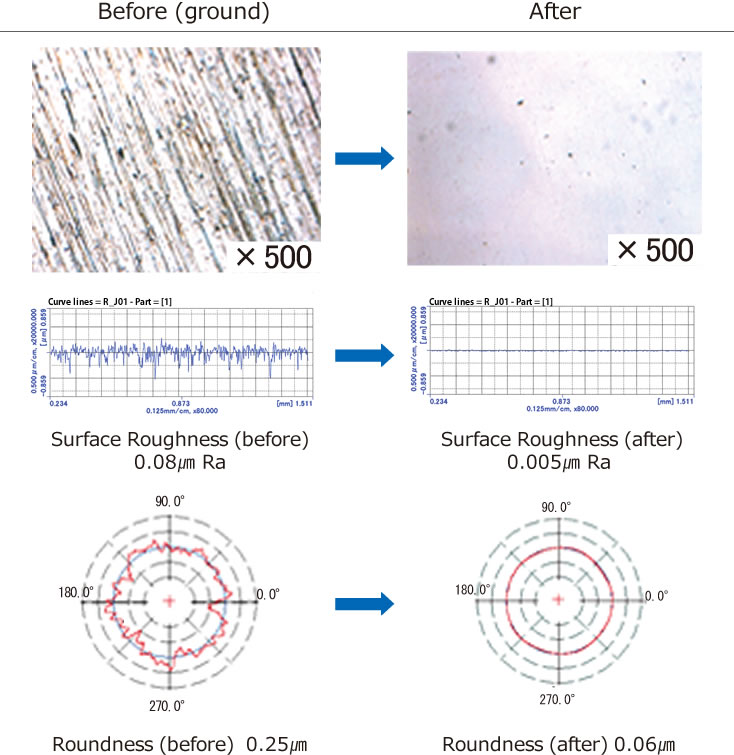
Consequently, Seibu's unique stone lapping methods generate low heat, and produce profile accuracy as well as nano-level accuracy of finished surface roughness.
It has also been confirmed that Seibu's unique stone lapping methods produce negative residual stress on the surface layers of workpieces. Seibu will continue research, development, and investigation on physical properties, in addition to study of profile accuracy, to verify the issues relating to residual stress.
OSCILLATION GUIDE USING AIR BEARINGS
CHARACTERISTICS OF AN OSCILLATION GUIDE USING AIR BEARINGS
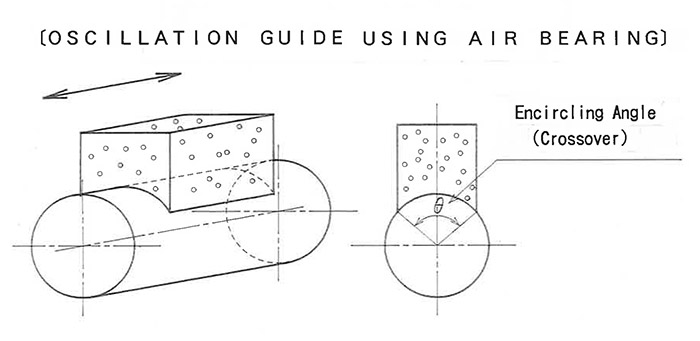
- The oscillation motion is parallel to the generating line.
- Form adjusting capability owing to a greater encircling angle.
- The phenomenon that occurs on a guide using a rolling element does not exist, owing to there being no metallic contact in the case of an oscillation guide using air bearings.
Highly efficient machining is also made possible with lower pressure and heat conditions. - A lapping stone with a lower level of hardness can be used, owing to dumping effects provided by the air bearings.
In the case of using an oscillation guide which uses air bearings, the grinding ratio of a lapping stone having a lower level of hardness can increase by 2 to 3 times compared to a guide using a rolling element.
OSCILLATION GUIDE USING ROLLING ELEMENTS
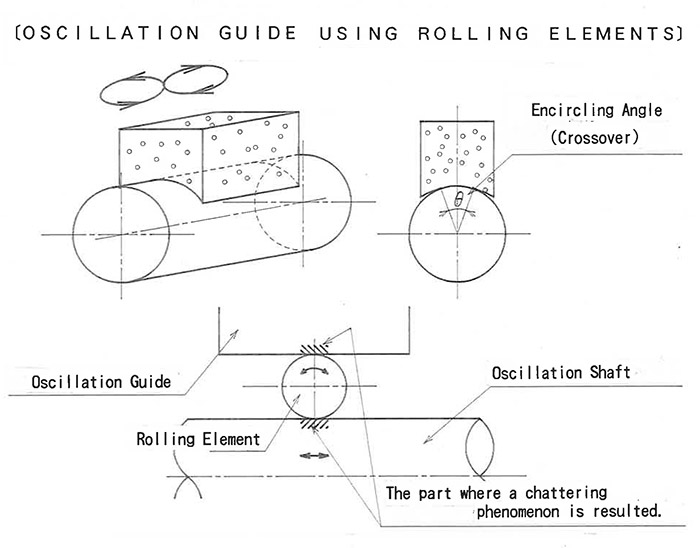
- In the case of an oscillation guide using rolling elements, Brinell impressions are generated on part of oscillation shaft due to slight movement of the rolling element as shown in the figure above.
- Therefore, a gap occurs in the oscillation guide, which results in circular arc movement in a horizontal direction, while a chattering phenomenon can also result in a vertical direction.
With the above results, the oscillation movement becomes a figure-eight movement in relation to the generating line, leading to a smaller encircling angle and reduced form-adjusting capability conforming to the prior process.
Results after stone lapping (roller outer diameter)